
Key Takeaways
- Instacart’s Revenue Model: Earns from delivery fees, memberships, advertising, and retailer partnerships.
- Strong Market Presence: Valued at $17B+, partners with major retailers, and serves millions.
- Convenience & Innovation: Offers same-day delivery, real-time tracking, and flexible pickup.
- Opportunities for Entrepreneurs: Replicating or integrating Instacart’s model can be profitable.
Did you know? Instacart generated $852 million in revenue in Q3 2024!
If you want to implement the Instacart business model to significantly boost your revenue, you’re in the right place!
In this blog, we’ll explore the Instacart business model and show you 6 proven ways to boost your earnings in the grocery delivery market.
Using this model, you can simplify grocery shopping for busy people. This approach allows customers to order groceries from anywhere, improving convenience while boosting efficiency and profitability.
The popularity of the Instacart business model is on the rise, and understanding how it works can help businesses grow.
So, let’s take a closer look at the details of this business model.
What is Instacart?
Instacart is the leading online grocery delivery and pickup service in North America, boasting a valuation of over $17 billion. It has more than 85,000 stores across North America. Also, they expanded their service and now operate in Canada.
The company partners with local, regional, and national grocery chains to deliver items to customers within hours. It has a large network of retailers, including major chains like Aldi, Kroger, Publix, Costco, and Walgreens.
Through its user-friendly app and website, Instacart allows customers to order groceries and essential items with ease. The company also provides alcohol delivery in states and provinces where it is allowed.
Moreover, the company offers customers a new way to discover and buy groceries and a new way for retailers to sell groceries.
| Category | Highlight |
| Founded | 2012 by Apoorva Mehta, Max Mullen, and Brandon Leonardo |
| Headquarters | San Francisco, California, USA |
| Service Area | United States and Canada |
| Retail Partners | 1,400+ retail banners, 85,000+ store locations |
| Active Users | 14M+ active users (2023) |
| Shoppers | 600,000+ independent contractors |
| Revenue Streams | Delivery fees, service fees, Instacart+ membership, advertising, retailer partnerships, product markups |
| Competitors | Amazon Fresh, Walmart Grocery, Shipt, DoorDash, FreshDirect |
Supercharge your deliveries with Enatega.
Register NowInstacart Facts and Statistics
- Instacart generated $3 billion in revenue in 2023 but made a net loss of $1.6 billion.
- With over 14 million active users in 2023, use Instacart.
- Instacart offers same-day delivery, which starts as early as 9 AM and runs as late as midnight.
How Does Instacart Work? A Step-by-Step Process
Below is the workflow of Instacart.
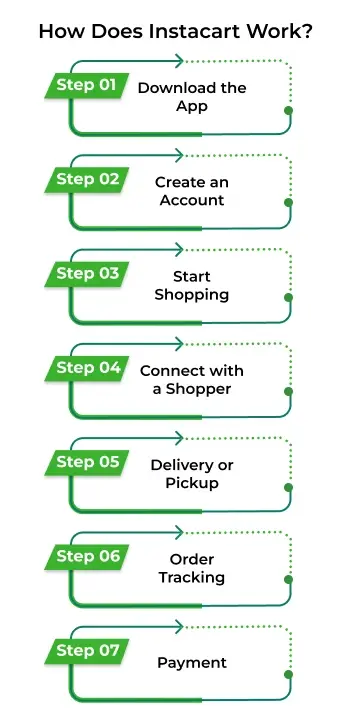
Download the App: Customers download the app onto their mobile phone from the App Store (iOS). They also place an order on the website by logging in with their credentials.
Create an Account: Create an account by providing the basic information, such as email and password.
Start Shopping: Customers shop for a variety of items from various stores such as Walmart, Costco, etc.
Connect with a Shopper: The app connects customers with a personal shopper in their area.
Delivery or Pickup: Customers can have their order delivered to their home, office, or any other place. They also select the curbside pickup at selected retail locations.
Order Tracking: Customers can track their orders and communicate with shoppers with an app or website.
Payment: Customers can pay for their order at checkout.
What is the Business Model for Instacart?
Instacart is known for delivering groceries and operates on a unique business model that combines several revenue streams.
Here are the key components of the Instacart cost structure.

Delivery Fees
- Customer Fee: Instacart charges customers delivery fees on every order that is placed using the app or website. It can vary based on order size, delivery time, and membership status. However, all orders must be at least $10 to qualify for delivery.
- Service Fee: In addition to delivery fees, customers often pay service fees that contribute to the overall cost of their orders. The service fee is not a tip and does not go to the rider who delivers the order.
The delivery fee charges are mentioned below.
| Order Amount | Delivery Charge |
| Orders above $35 | Regular or 2-hour delivery costs $3.99, and 1-hour delivery costs $5.99 |
| Orders under $35 | Regular or 2-hour delivery costs $7.99, and 1-hour delivery costs $9.99 |
| Instacart+ members | Free delivery on orders of $35 or more per retailer |
| Priority delivery | Starts at $2 and has a shorter delivery time of 60 minutes or less |
Instacart Express Membership
Customers can subscribe to Instacart+, which costs $9.99 per month or $99 per year. Instacart+ can help save time and money. It offers several benefits, like:
- Unlimited free delivery on orders of at least $35
- Peacock premium subscription
- 5% credit back, with some restrictions
Partnerships with Retailers
Instacart partners with various grocery and retail chains, allowing them to offer online shopping and delivery through Instacart’s platform. Retailers pay Instacart for this service, which helps them reach online customers without developing their own infrastructure.
Advertising Revenue
It is another Instacart business plan model. Retailers can pay for advertising on the Instacart platform to promote their products to customers. This includes sponsored listings and featured placements.
In 2022, nearly 30% of Instacart’s revenue was from advertising.
Instacart offers different advertising strategies to drive sales and help brands engage with customers. These are:
- Sponsored Products: Brands can promote specific products within the Instacart platform, increasing visibility and driving sales through targeted placements.
- Display Ads: These ads appear on various pages of the Instacart site, allowing brands to reach customers.
- Search Ads: Brands can bid on keywords to appear at the top of search results, ensuring their products are seen first by potential buyers.
- Promotions and Discounts: Brands can run special promotions, such as discounts or limited-time offers, to entice customers and boost sales.
- Brand Pages: Dedicated brand pages allow companies to showcase their products, tell their story, and engage directly with customers.
- Retargeting Ads: Instacart uses data to retarget users who have previously engaged with a brand, reminding them of products they may want to purchase.
Product Markup and Fees
Instacart may also earn revenue from product markups or additional fees on certain items. The fees can vary depending on the retailer.
Instacart applies a markup of 15% or more on the items sold through its platform. This markup contributes to Instacart’s revenue, which is then used to pay the customers. However, not all retailers on Instacart disclose this markup.
Some retailers, such as Whole Foods, collaborate with Instacart and ensure no markup is applied. Other retailers, like Costco, do impose a markup. For instance, one shopper noted a 24% markup on a Costco order made via Instacart.
Grocery Pickup Services
Instacart offers grocery pickup services, allowing customers to order online and pick up their groceries at a designated location, often for a fee.
How Does Instacart Make Money?
Instacart makes a profit using different models, such as:
- Marketplace business model
- Commission-based business model
- Software as a service (SaaS) business model
- Transaction-based business model
- Advertising-based business model
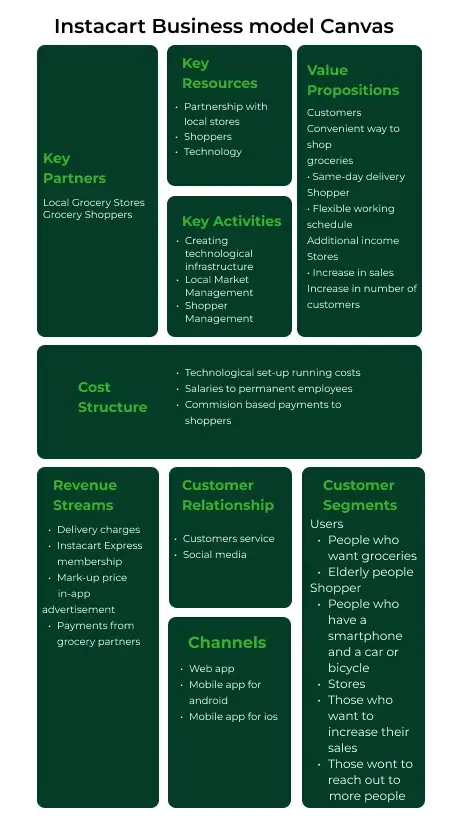
Instacart Business Model Canvas
Below is an Instacart business model canvas.
Features of Building an App Like Instacart
Features can make the app successful and add unique value to it. It is an important thing that differentiates your app from your competitors. Therefore, always offer something distinct and valuable to your customers.
The following are the features that you should incorporate in the Instacart clone app.
| Customers | Retail Partners | Riders | Admin Dashboard |
| Sign Up | Sign Up | Registration | Payment management |
| Search and Filter | Order management | Route optimization | Commission management |
| Order cancellation | Inventory management | Chat/call with the customer | Reports and analytics |
| Delivery tracking | Product listing | Accept/Reject order | |
| Return and replacement | |||
| Contactless delivery |
Instacart Competitors’ Analysis
Below is a comparison analysis of Instacart and its competitors.
| Competitor | Strengths | Weaknesses | Market Position |
| Amazon Fresh | Backed by Amazon’s massive logistics, Prime integration, and wide product variety | Limited to Amazon Prime members in select areas; struggles with perishable delivery quality | Strong global brand, aggressive expansion in grocery delivery |
| Walmart Grocery | Huge store network, competitive pricing, curbside pickup, strong rural presence | Delivery speed is slower than Instacart in some regions; less flexible delivery windows | Leading U.S. grocery retailer with growing online adoption |
| Shipt (Target-owned) | Strong integration with Target, fast delivery, user-friendly app | Smaller retailer network compared to Instacart; limited geographic reach | Niche player but solid in Target-heavy regions |
| FreshDirect | Focused on high-quality fresh produce, a loyal customer base in the Northeast U.S. | Limited geographic reach; higher prices | Strong regional player but lacks Instacart’s national scale |
| Uber Eats (Grocery) | Uses a global delivery network, integrates food + grocery delivery in one app | Grocery delivery is not its core focus; the retailer network is weaker than Instacart | Secondary grocery option for Uber Eats users, growing steadily |
Instacart Challenges
Instacart’s business model has driven rapid growth. However, it also faces several challenges, such as:

High Operating Costs
- Managing logistics, delivery fleets, and order fulfillment is expensive.
- Even with multiple revenue streams, rising fuel costs, labor expenses, and technology upgrades put pressure on margins.
Thin Profit Margins
- Grocery delivery has low profit margins compared to other industries.
- Heavy reliance on promotions, discounts, and competitive pricing makes it difficult to maintain consistent profitability.
Dependence on Gig Workers
- Instacart relies heavily on independent contractors (shoppers).
- Issues like worker dissatisfaction, legal disputes over classification, and fluctuating labor availability can disrupt operations.
Intense Competition
- Competitors like Amazon Fresh, Walmart Grocery, DoorDash, and Shipt are aggressively expanding.
- These companies often have stronger logistics networks and larger customer bases.
Pricing and Customer Complaints
- Markups on certain products (sometimes 15–25%) and service fees make Instacart more expensive than in-store shopping.
- Many customers complain about hidden costs and varying produce quality due to the shopper’s selection.
Retailer Dependency
- Instacart doesn’t own inventory; it relies on partnerships with retailers.
- If a major retailer ends its partnership (like Whole Foods did after Amazon’s acquisition), it poses a big risk to Instacart’s model.
Scalability and Sustainability
- Scaling beyond urban areas is difficult due to lower-order volumes in rural markets.
- Ensuring fast delivery across all geographies is a constant logistical challenge.
FAQs
1. How to start an Instacart business?
Below are some steps to help you start an Instacart business.
- Go to instacart.com/business
- Create the business profile (It is free to create and use)
- Add your business email address, name, and type. Then, your account is created.
2. What percentage does Instacart take?
Instacart service fees start at 5% and it does not apply to pickup orders. The service fee supports the platform and covers a range of operating costs, such as:
- Shopper operations
- Insurance
- Background checks
- Customer support
3. Why is Instacart so successful?
Instacart is successful due to these reasons:
- User-friendly platform that offers convenience and time savings for customers
- Partnerships with major grocery chains
- Wide selection of options
- Fast delivery
4. Who is Instacart’s competition?
Instacart’s main competitors include Amazon Fresh, Walmart Grocery, Shipt, FreshDirect, and DoorDash. These services also offer grocery delivery and pickup options, competing for market share in the online grocery sector.
5. What is the difference between Instacart and Instacart+?
Instacart is the standard grocery delivery service, while Instacart+ is a subscription plan offering free delivery on orders over a certain amount, reduced service fees, and exclusive promotions.
6. What is the downside of Instacart?
One downside of Instacart is the high service fees and tips that can increase the overall cost of groceries. Additionally, the quality of fresh produce may vary, as it depends on the individual shopper’s selection.
7. Is Instacart cheaper than DoorDash?
Instacart can be cheaper than DoorDash for grocery shopping, as it charges lower delivery fees for groceries. However, DoorDash may offer promotions or discounts for restaurant deliveries, so the cost comparison can vary based on specific orders and locations.
8. How much does Instacart charge per delivery?
Instacart charges delivery fees ranging from $3.99 to $7.99 for orders over a certain amount, but fees can be higher for smaller orders. Additionally, there may be service fees and tips, which can increase the total cost.
Supercharge your deliveries with Enatega.
Register NowConclusion
Implementing an Instacart business model helps you generate revenue.
If you run a grocery delivery business and want to adopt the Instacart revenue model, but still have some confusion, you can consult Enatega. We help you in helping in your business and provide you with a tailored online grocery delivery software to help you earn more profit.
So, book a free demo and hire the developers who can build the best app.















 IOS
IOS Android
Android Web
Web




