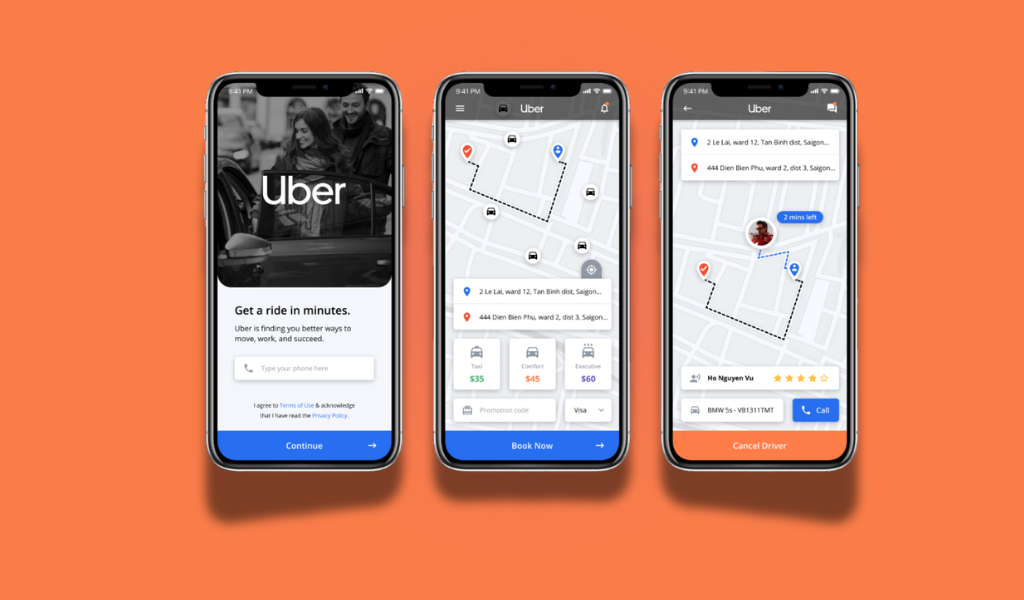
The days of waving down taxis or waiting endlessly for a ride are long gone. Today, with just a few taps on your smartphone, you can book a car, see your driver’s location, and pay digitally all within seconds.
This experience is made possible by ride-hailing apps, and Uber is the name that started it all. It didn’t just change how we travel; it redefined urban mobility and set the benchmark for the entire on-demand transportation industry.
If you’re an entrepreneur with a vision to build the next big ride-hailing platform, this blog is your roadmap. From understanding Uber’s business model and core features to exploring the technology, development process, and costs involved, we’ll cover everything you need to know.
So, let’s dive in and explore how to build an app like Uber that stands out in today’s competitive market.
Supercharge your deliveries with Enatega.
Register NowWhat is Uber?
Uber is a global ride-hailing platform that connects passengers with drivers through a mobile app. It makes transportation faster, easier, and more convenient.
Founded in 2009 in San Francisco, Uber disrupted the traditional taxi industry by introducing an on-demand model where users can instantly book a ride, track their driver’s location in real time, and pay through the app.
Beyond its core ride-hailing service, Uber has expanded into multiple verticals, including Uber Eats (food delivery), Uber Freight (logistics), and even autonomous vehicle research.
The company operates in over 70 countries and serves millions of users daily, offering various ride options such as UberX, UberXL, and Uber Black to cater to different budgets and preferences.
How Does the Uber App Work?
Below is the working of the Uber app.

1. Request a Ride
A user opens the Uber app, enters their destination, and chooses a ride type (like UberX, UberXL, or Uber Black). The app automatically calculates the estimated fare and expected arrival time.
2. Matching with a Driver
Once the request is made, the app’s algorithm searches for the nearest available driver. When a driver accepts the request, the rider receives details about the driver, vehicle, and estimated time of arrival.
3. Real-Time Tracking
Both the rider and the driver can track each other’s locations using GPS. Riders can also share their live trip status with friends or family for safety.
4. Easy Payment
After reaching the destination, the fare is automatically charged to the rider’s chosen payment method (credit card, digital wallet, or cash, depending on the region). The app handles fare calculation and payment processing securely.
5. Ratings and Feedback
At the end of the trip, both rider and driver rate each other based on their experience. These ratings help maintain service quality and build trust within the platform.
Uber Business Model – How Uber Makes Money?
The Uber business model is built around the concept of a two-sided marketplace that connects drivers (service providers) with riders (customers) through a mobile platform.
Uber doesn’t own any vehicles; instead, it acts as an intermediary, using technology to match supply (drivers) and demand (riders) efficiently.
Here is the process that shows how Uber’s business model works.
Value Proposition
- For Riders: A fast, convenient, and reliable way to get from point A to B at transparent prices.
- For Drivers: A flexible income opportunity with minimal barriers to entry and access to a large pool of passengers.
Key Components of Uber’s Business Model
- Users: Riders who need transportation.
- Drivers: Independent contractors who provide the rides.
- Platform: The Uber app that facilitates ride requests, navigation, payments, and communication.
Revenue Model
Uber earns money through several methods, which include:
- Commission per ride: Uber takes a percentage (usually 20–30%) from each trip’s total fare.
- Surge pricing: Dynamic pricing increases fares during high-demand periods, increasing revenue.
- Subscription plans: Uber Pass and Uber One offer discounts and exclusive benefits for a monthly fee.
- Cancellation fee: They also generate revenue by charging the riders for canceling the ride after a specific period of time.
- Other streams: Uber Eats (food delivery), Uber Freight (logistics), and advertising within the app also contribute to revenue.
Benefits of Creating an App Similar to Uber
Dreaming of creating a local Uber? An Uber with a twist? An Uber competitor?
But, wait, before starting, you have to know what benefits come with creating a car booking app similar to Uber.
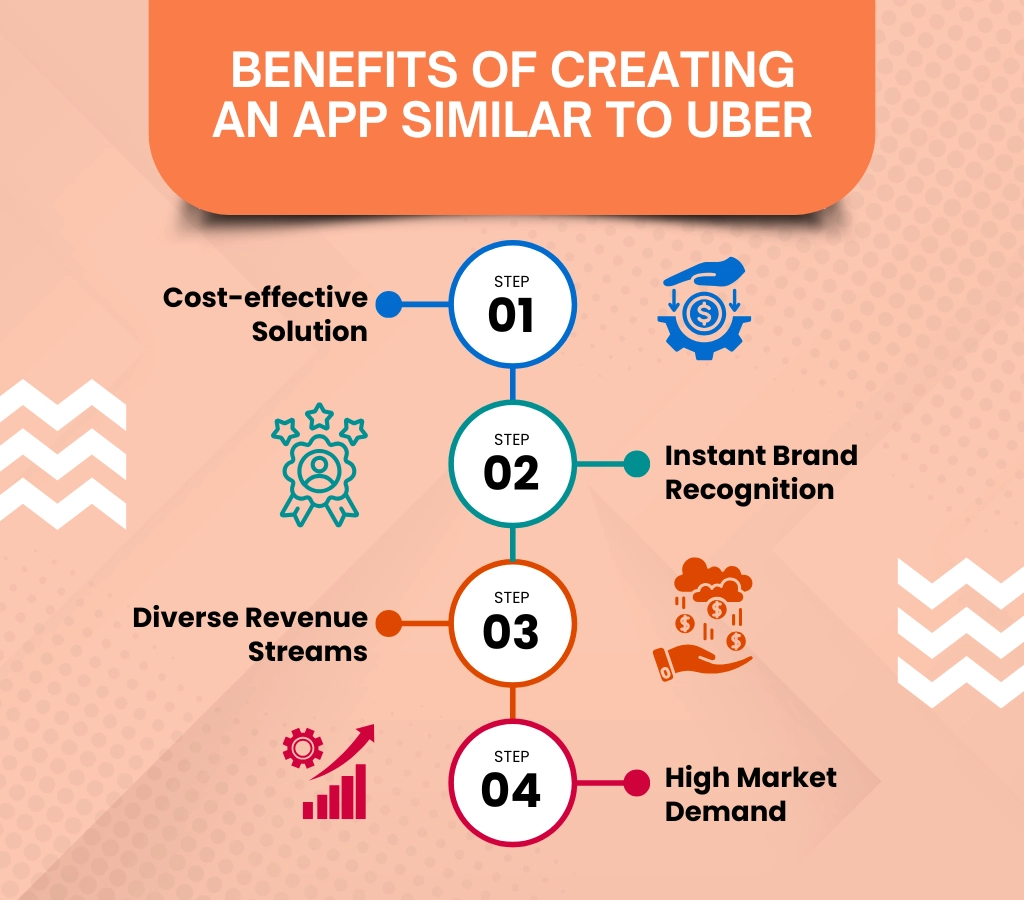
Cost-effective Solution
Developing a ride-hailing app can save you money in the long run. By using existing technologies and platforms, you can minimize initial costs.
Instant Brand Recognition
The ride-hailing industry is growing, and by creating an app that meets the needs of users, you can quickly establish your brand in a competitive market. With the right marketing strategies, your app can gain visibility.
Diverse Revenue Streams
A well-designed app offers multiple monetization options, such as ride fares, premium services, and partnerships. This variety can help secure a steady revenue flow and increase profitability.
High Market Demand
The demand for convenient transportation solutions continues to rise. With more people looking for alternatives to traditional taxis, your app can meet the needs of modern commuters.
How to Build an Uber Clone App?
Building an Uber clone app requires careful planning, strategic decisions, and the right blend of technology and execution. Whether you’re opting for a no-code platform or traditional app development, following a structured approach is essential.
Below are some steps to help you in the Uber clone app development phase.
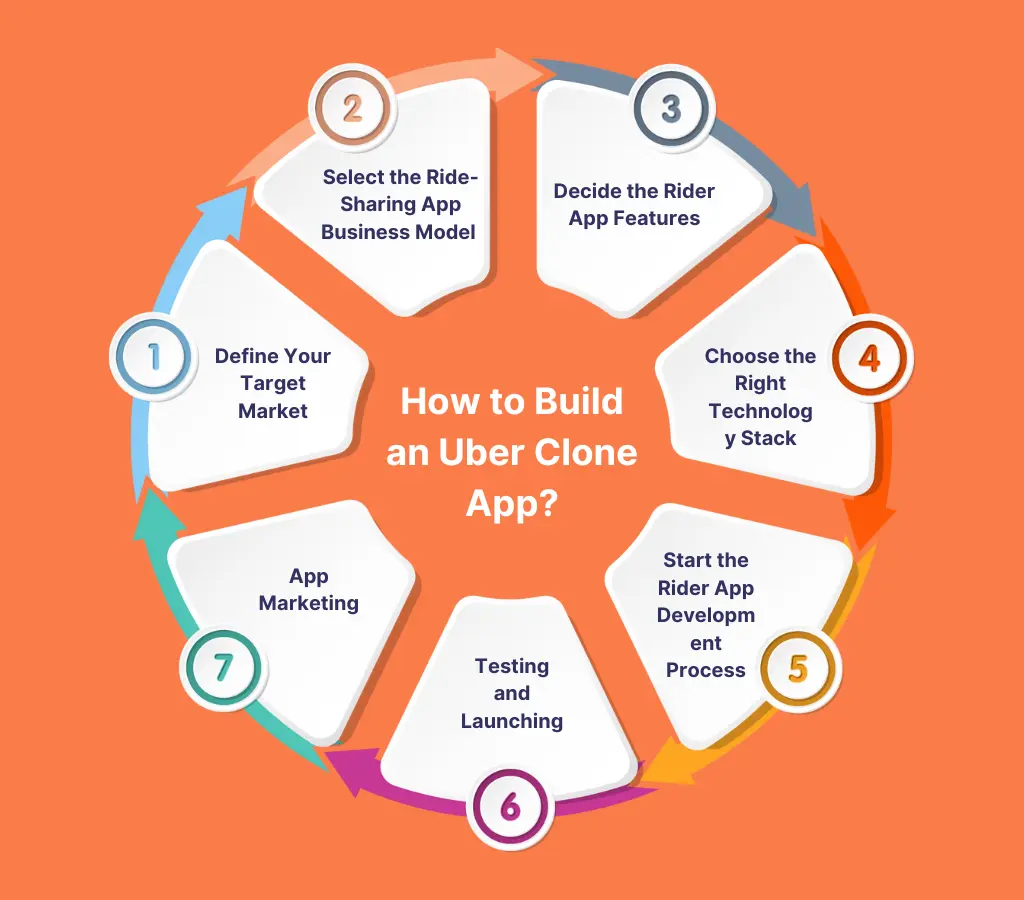
1. Define Your Target Market
Before starting the development, begin with market research. Understanding your target audience, their transportation needs, and market trends will shape your app’s foundation.
Start by selecting a specific region or country to launch in. Each market differs in economy, urban density, and transportation preferences. For instance, a city with heavy traffic might not be ideal for car-based ride-sharing, but could be with bike or scooter options.
Study your competitors, identify existing ride-hailing services, and analyze why previous ventures may have failed. Factors such as regulations, pricing, or infrastructure limitations could influence your strategy.
2. Select the Ride-Sharing App Business Model
Once you understand your market, define how your business will operate and generate revenue. This step involves:
- Identifying user personas (drivers, riders, and admins).
- Mapping user journeys and scenarios to visualize app interactions.
- Creating a business model canvas and value proposition canvas to refine your goals.
Many startups skip this phase, but it’s important. Conducting product workshops helps clarify your business vision.
You should also develop user stories, detailed descriptions of each feature, and how users will interact with them. This step helps in accurate time and cost estimation later during development.
3. Decide the Rider App Features
Your car booking solution should include core features that benefit both riders and drivers. Here are some features that must be included in the ride-hailing app, like Uber.
For Rider App
- Easy sign-up and authentication
- Ride booking and real-time tracking
- Fare estimation
- Multiple payment options
- Ratings and reviews
- Trip history and support
- Trip cancelling
- Push notifications
- Vouchers and friend-invite promotions
- Trip scheduling
- Multi-language support
- Booking history
For Driver App
- Profile verification
- Ride requests and navigation
- Earnings dashboard
- Availability toggle
- Trip records
For Admin Dashboard
- Rider management
- Trip management
- Compliant handling
- Revenue tracking
- Payment management
- Notification management
- Vehicle management
- Zone management
4. Choose the Right Technology Stack
Selecting the right technology stack will determine your app’s performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. A well-chosen stack ensures high performance and stability under heavy loads, allowing the app to handle user growth without performance degradation.
Here is the tech stack used in building the app like Uber.
- Frontend: Flutter or React Native for cross-platform apps.
- Backend: Node.js, Django, or Laravel.
- Database: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or Firebase.
- APIs: Google Maps API (for navigation), Twilio (for communication), Stripe or PayPal (for payments).
- Hosting: For hosting, use AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure to ensure your app handles peak traffic and grows smoothly.
Below are some factors to consider when selecting a stack.
- Project requirements
- Budget
- Security needs
- Time-to-market
- Expertise of the development team
5. Start the Rider App Development Process
Once your strategy and features are finalized, move on to app design and development. Begin by creating wireframes and UI/UX prototypes to visualize your app’s flow.
Then, build an MVP (Minimum Viable Product), a simplified version of your app that includes essential features. Launching an MVP allows you to gather feedback, attract early users, and make improvements without overspending on unnecessary functionality.
6. Testing and Launching
Thorough testing ensures your app runs smoothly across devices and platforms. This process identifies and fixes bugs, performance issues, and usability problems early.
You have to focus on:
- Functionality testing (core features)
- Performance testing (speed and scalability)
- Security testing (data protection and payment safety)
- User acceptance testing (UAT) before public release
Once tested and refined, publish your app on the Google Play Store and the Apple App Store.
7. App Marketing
After launch, it’s time to spread the word. Implement a marketing strategy that includes:
- App Store Optimization (ASO)
- Social media marketing
- Referral programs and promo codes
- Collaborations with local drivers or transport services
Monitor analytics and user feedback to continuously improve your app and maintain user retention.
How Much Does it Cost to Develop an App Like Uber?
The cost to develop an app like Uber ranges from $40,000 for a basic MVP to over $300,000 for a fully-featured, enterprise-level solution.
The total investment depends on several factors, including:
- App’s complexity
- Target platforms
- App features
- Design quality
- Location of your development team
Below is a rough estimate to help you plan your budget more accurately.
| App Type | Cost | Timeline |
| Basic Minimum Viable Product (MVP) | $40,000 – $60,000 | 2 – 3 months |
| Mid-Range Custom App | $70,000 – $150,000 | 6 – 9 months |
| Advanced or Enterprise-Level App | $150,000 – $300,000+ | 9 – 18 months |
| Uber Clone Script | $15,000 – $50,000 | 1 – 3 months |
Factors Influencing the Cost of Taxi Booking Solution App
Several critical factors determine the overall budget for your Uber-like app:
| Factor | Cost Impact | Details |
| Development team and location | High | Hiring developers in North America or Western Europe ($80–$250/hr) costs more than teams in South Asia or Eastern Europe ($20–$70/hr). |
| App platform | High | Native development for iOS and Android is pricier than cross-platform frameworks (e.g., Flutter, React Native). |
| Features and functionality | High | Complex features like AI-based pricing, analytics, or route optimization increase both time and cost. |
| Design (UI/UX) | Medium | A custom, premium interface with animations costs more than a simple, template-based design. |
| Backend infrastructure and APIs | High | A strong backend must handle real-time requests, integrate APIs (Google Maps, Stripe, Twilio), and scale as usage grows. |
| Testing and QA | Medium | Ensures stability, performance, and security; usually accounts for 15–20% of total development costs. |
| Maintenance and support | Annual | Ongoing costs for updates, hosting, and bug fixes equal 15–20% of the initial development cost per year. |
FAQs
1. How long does it take to build an app like Uber on android or iOS platform?
To build a complex, full-featured app like Uber for both Android and iOS, the process takes anywhere from 9 to 18 months or more. This timeline varies and depends heavily on the app’s complexity, the number of features, and other factors. A simpler MVP version can sometimes be completed in as little as 3 to 6 months.
2. Which app makes more money, Uber or Lyft?
Uber makes more money than Lyft, with higher revenue and broader services that include ridesharing, food delivery, and freight.
3. What platform is Uber built on?
Uber is primarily built using a combination of Node.js, Python, and Java for backend services, with React Native and Swift/Kotlin for mobile app development, supported by AWS and Google Cloud for scalable infrastructure.
4. Is there a competitor to Uber?
Yes, the main competitor to Uber is Lyft, which offers similar ride-hailing services in many U.S. cities. Other alternatives exist in different regions, such as Ola and Bolt.
Supercharge your deliveries with Enatega.
Register NowConclusion
Creating an app like Uber is more than just developing software; it’s about designing a smart, scalable system that solves real-world transportation challenges. The journey involves careful planning, research, and execution; the payoff can be extraordinary when done right.
With the right development partner, you can change your ride-hailing idea into a fully functional, user-centric platform. At Enatega, we specialize in building powerful and intuitive car booking apps that help businesses go digital and grow faster.
Book a free demo with Enatega today and see how we can help you launch a successful, Uber-like app built for the future of mobility.















 IOS
IOS Android
Android Web
Web




